


The Return of Natural Theology

Richard Sternberg on the Trail of the Immaterial Genome

Brian Miller: The Surprising Relevance of Engineering in Biology
Today’s ID the Future brings listeners physicist and engineer Brian Miller’s recent lecture at the Dallas Conference on Science and Faith, “The Surprising Relevance of Engineering in Biology.” Miller rebuts several popular arguments for evolution based on claims of poor design in living systems, everything from the “backward wiring” of the vertebrate eye to whales, wrists, ankles, and “junk DNA.” But the main emphasis of this discussion is the exciting sea change in biology in which numerous breakthroughs are occurring by scientists who are treating living systems and subsystems as if they are optimally engineered systems. Some in this movement reject intelligent design for ideological reasons. Others embrace it. But all systems biologists treat these systems as if they are masterfully engineered systems, and that perspective is rapidly accelerating progress in experimental biology. At the forefront of this work is the Conference on Engineering in Living Systems (CELS). Miller provides an exciting sneak peek at some of the cutting edge research from members of this group.

Neil Thomas Takes on Epicurus and the Logical Positivists
Today’s ID the Future concludes a three-part series featuring author Neil Thomas in a free-ranging conversation with radio show host Hank Hanegraaff. The focus is Thomas’s recent book, Taking Leave of Darwin: A Longtime Agnostic Discovers the Case for Design. Here Thomas and Hanegraaff discuss the logical positivists and what Thomas sees as their failure to consistently apply their evidential standards to Darwinism. Thomas also contrasts the cosmic nihilism of Richard Dawkins with the mounting evidence of fine tuning for life, and calls out what Thomas describes as the magical thinking at the heart of Darwinism. Hanegraaff and Thomas also explore how Darwin’s theory of evolution has roots in an ancient philosophical system that was long regarded as resting on such flimsy speculative foundations that it wasn’t taken seriously for long centuries. In Thomas’s opinion, that philosophical system shouldn’t have been taken seriously then, and still shouldn’t be. In the wrap up, Hanegraaff and Thomas provide a model of how two men with differing positions on Christianity can converse and even challenge each other while remaining cordial. Hanegraaff, an Orthodox Christian, urges Thomas, a longtime agnostic rationalist who has recently become open to theism, to take his journey into theism further by considering the historical claims specific to Christianity. Does Thomas bridle? Not all. Listen in to hear how the conversation plays out, and find Thomas’s book, which Hanegraaff highly recommends, here. This three-part series is posted here by permission of Hank Hanegraaff. For more Hank Hanegraaff, check out his podcast, Hank Unplugged.

New Book on Thomas Reid’s Common Sense Design Philosophy

Stephen Meyer Introduces His New Course on Intelligent Design
On this episode of ID the Future, bestselling author and Center for Science and Culture director Stephen Meyer introduces an exciting and informative new Discovery U video course, “Stephen Meyer Investigates Scientific Evidence for Intelligent Design.” Here he sets the stage by recalling a few times when ID made national news headlines, sometimes with Meyer right in the middle of the controversy. He also addresses some of the questions generated by these dustups: Is ID faith-based or science-based? Did the earliest scientists follow ID principles or did they avoid them, as one state education commissioner claimed. And why did two highly regarded research scientists get expelled from their museum positions, and were the expulsions justified?

Aeschliman Talks C. S. Lewis, The Abolition of Man, and That Hideous Strength
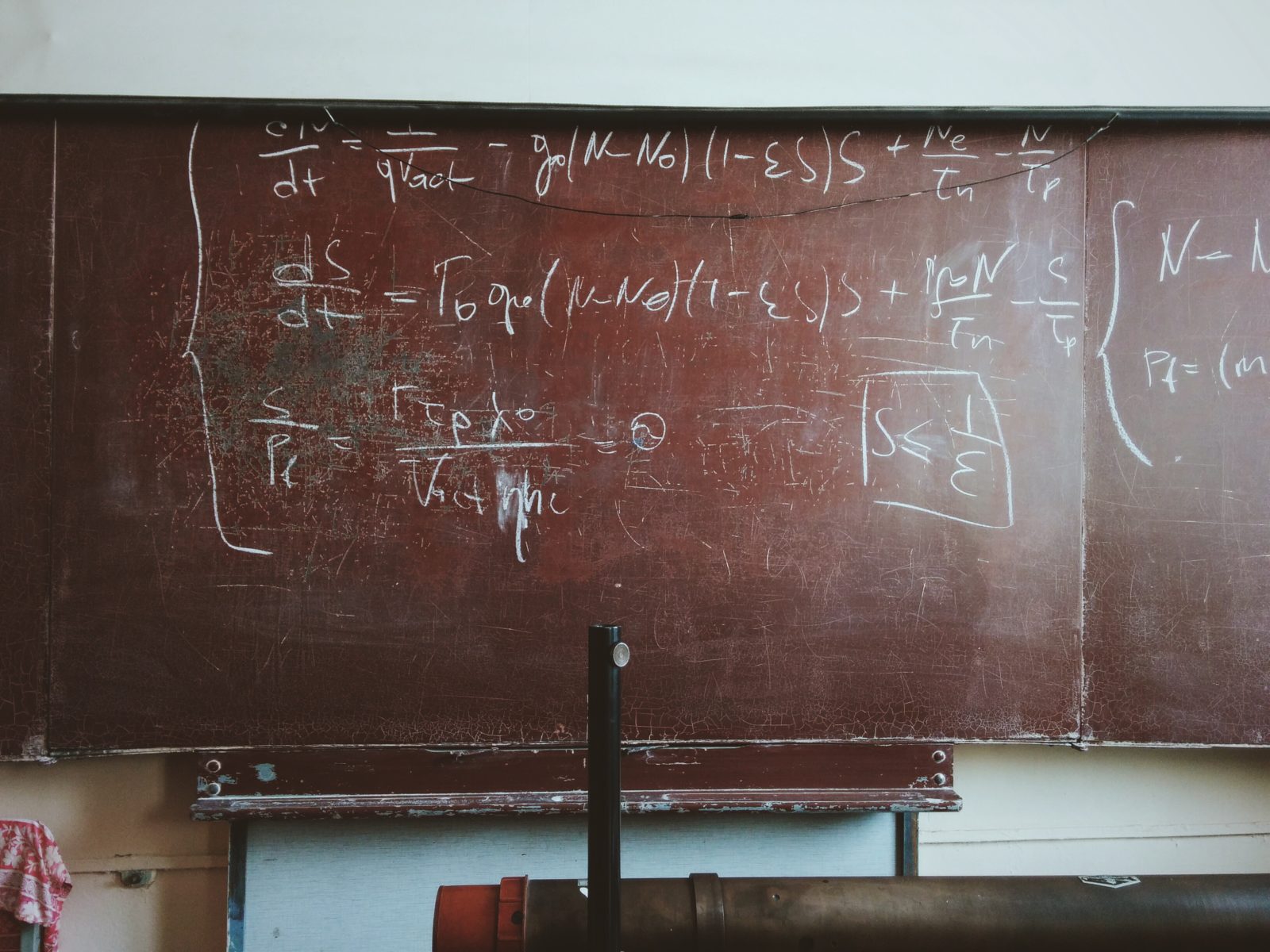
Richard Sternberg on the Trail of the Immaterial Genome
On this episode of ID the Future, Dr. Richard Sternberg, research fellow at the Biologic Institute, speaks on his mathematical/logical work showing the difficulty of identifying genes purely with material phenomena, and that DNA doesn’t have all that’s needed to direct the development of organisms.
Read More ›Kepler, Galileo, the Book of Nature, and the First Mathematician
On this episode of ID the Future, Andrew McDiarmid talks with science historian Michael Keas on pioneering mathematical astronomer Johannes Kepler, based on Keas’ new work from ISI Books, Unbelievable: 7 Myths About the History and Future of Science and Religion. Kepler studied theology before turning to math and science, and it was his belief in God that guided his extraordinary discoveries. “Without an architect who created the world,” he said, “there is no … power in mathematics to make anything material.” Scientists, in his view of God, were thinking the thoughts or ideas that God himself had thought any time they discovered some law or deep pattern in nature. Kepler is just one of a long list of great early scientists, including Galileo, who saw a “book” of God’s revelation in nature written in the language of mathematics. God designed the world for discovery, Kepler believed, and that conviction inspired his groundbreaking investigations.
Read More ›