


Sex: A Masterpiece of Design

Fooled by Darwinism: One Scholar’s Cautionary Tale

Michael Behe: Behind The Scenes of Secrets of the Cell

Michael Behe on the Origin of Biological Information
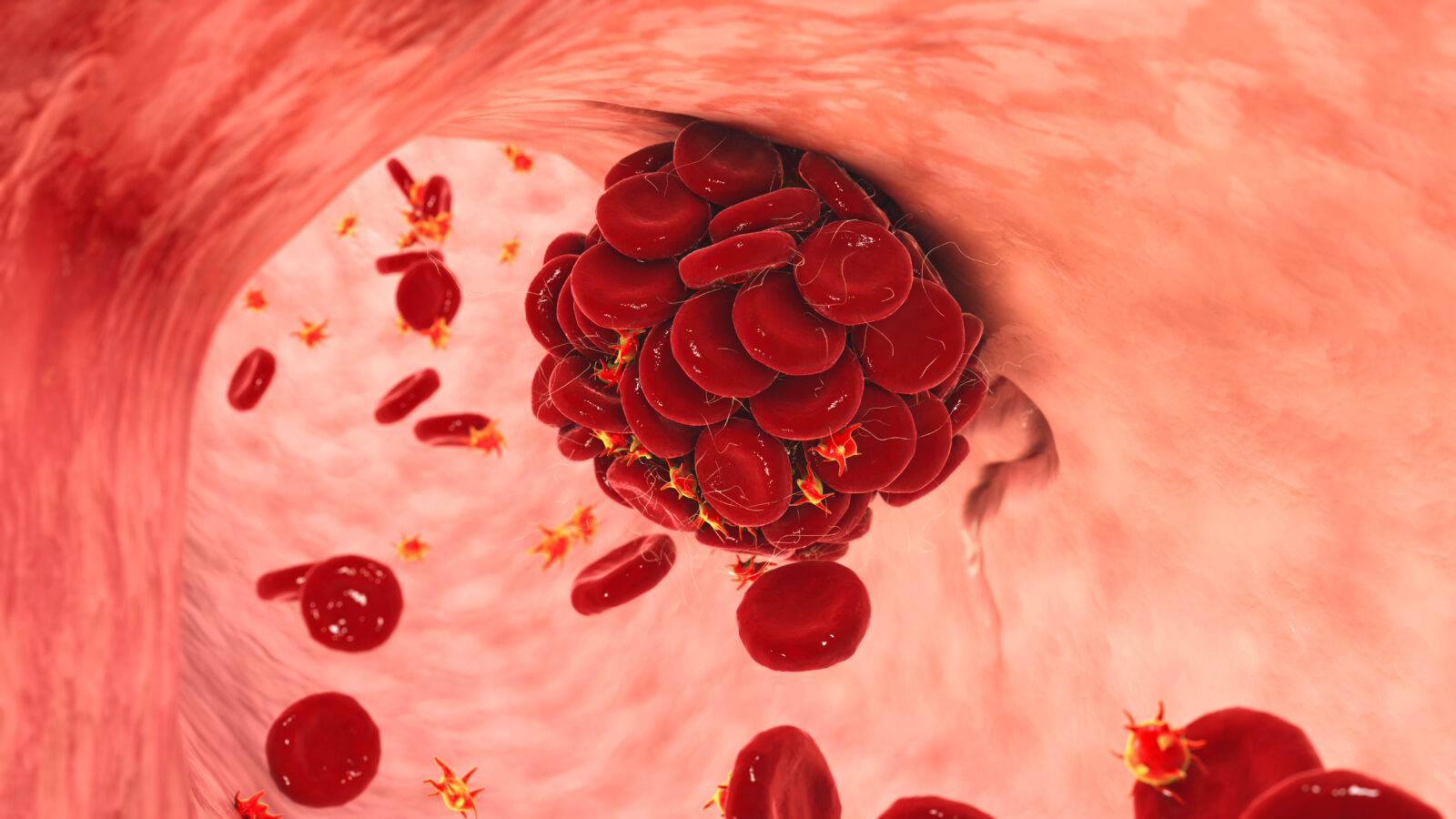
The Engineering Prowess of the Blood Clotting Cascade

The Return of Natural Theology

Chimp and Human Genomes: An Evolution Myth Unravels
On today’s ID the Future, Casey Luskin rebuts the oft-repeated claim that the human and chimp genomes are 98-99% similar and therefore surely resulted from Darwinian common descent. Luskin cites an article in the journal Science which describes the 98-99% claim as a myth. The original figure was derived from a single protein-to-protein comparison, but once you compare the entire genomes, and use more rigorous methods, the similarity drops several percentage points, and on one account, down into the mid-80s. Additionally, the chimp genomes used in the original comparison studies borrowed the human genome for scaffolding, thus artificially boosting the degree of similarity. What about supposed junk DNA similarities between human and chimp? Why would an intelligent designer put the same useless “pseudogene” in both the original chimp population and original human population? Surely a better explanation, the evolutionists argue, is Darwinian common ancestry. The problem with that argument, according to Luskin, is that pseudogenes are turning out to have functions. In other words, they aren’t, as evolutionists had assumed, just so much junk DNA. One example: evolution advocates Kenneth Miller and Eugenie Scott cited the beta-globin pseudogene as knockdown evidence of common descent between humans and apes. But the beta-globin pseudogene, it turns out, is essential for producing red blood cells. This means that finding this gene in both apes and humans is no more indicative of mindless common descent than finding wheels on both cars and airplanes. An intelligent designer would be expected to use the successful design element in both cases. Luskin provides still other lines of evidence undercutting the DNA-similarity argument for chimp-human common ancestry. Tune in to hear it all. And to read Luskin’s latest work on the subject, get the new free online ID book from South Africa, Science and Faith in Dialogue, with contributions from Luskin, Stephen Meyer, Hugh Ross, Guillermo Gonzalez, James Tour, Fazale Rana, Marcos Eberlin, and others.

Ann Gauger: A Scientist’s Journey into the Intelligent Design Movement
On today’s ID the Future, biologist and intelligent design researcher Ann Gauger tells host Eric Anderson the rest of her story about how she was drawn into the intelligent design movement. The two discuss everything from the challenges she faced making it in a male-dominated field to the evidential power of beauty in the natural world. But how did she end up in the ID movement? After stepping out of a promising career as a research scientist to focus on her family and meeting the needs of an autistic child, she assumed that her life as a scientist was behind her. But then several years later she began reading the work of Darwin skeptics and intelligent design trailblazers—Phillip Johnson, Jonathan Wells, Michael Behe, and others—and then she realized they were all associated with a think tank, Discovery Institute’s Center for Science and Culture, just down the street from where she lived. She eventually signed DI’s Dissent from Darwin list, then a year or so after that she signed up for a regular ID newsletter, Nota Bene, signing her name “Ann Gauger, PhD.” She got a phone call from someone at Discovery Institute twenty minutes later. The rest of the story is by turns comical, inspiring, and touching. Before wrapping up her story she urges young women scientists to not let themselves get pressured out of contributing just because STEM fields tend to be male dominated. And she shares a story of being accused at a public university event of lying and suppressing research evidence that supposedly supported evolutionary theory. Not true, she explains.
Your Designed Body: “Irreducible Complexity on Steroids”
On today’s ID the Future, Your Designed Body co-author and physician Howard Glicksman talks with host and neurosurgery professor Michael Egnor about Glicksman’s new book, co-authored with systems engineer Steve Laufmann. Glicksman walks through a series of systems in the human body that are each irreducibly complex, and are each part of larger coherent interdependent systems. As Glicksman puts it, the human body is “irreducible complexity on steroids.” How could blind evolutionary processes, such as neo-Darwinism’s joint mechanism of natural selection working on random genetic mutations, build this bio-engineering marvel? Your Designed Body makes the case that it couldn’t. It’s not even close. What is required instead is foresight, planning, and engineering genius.