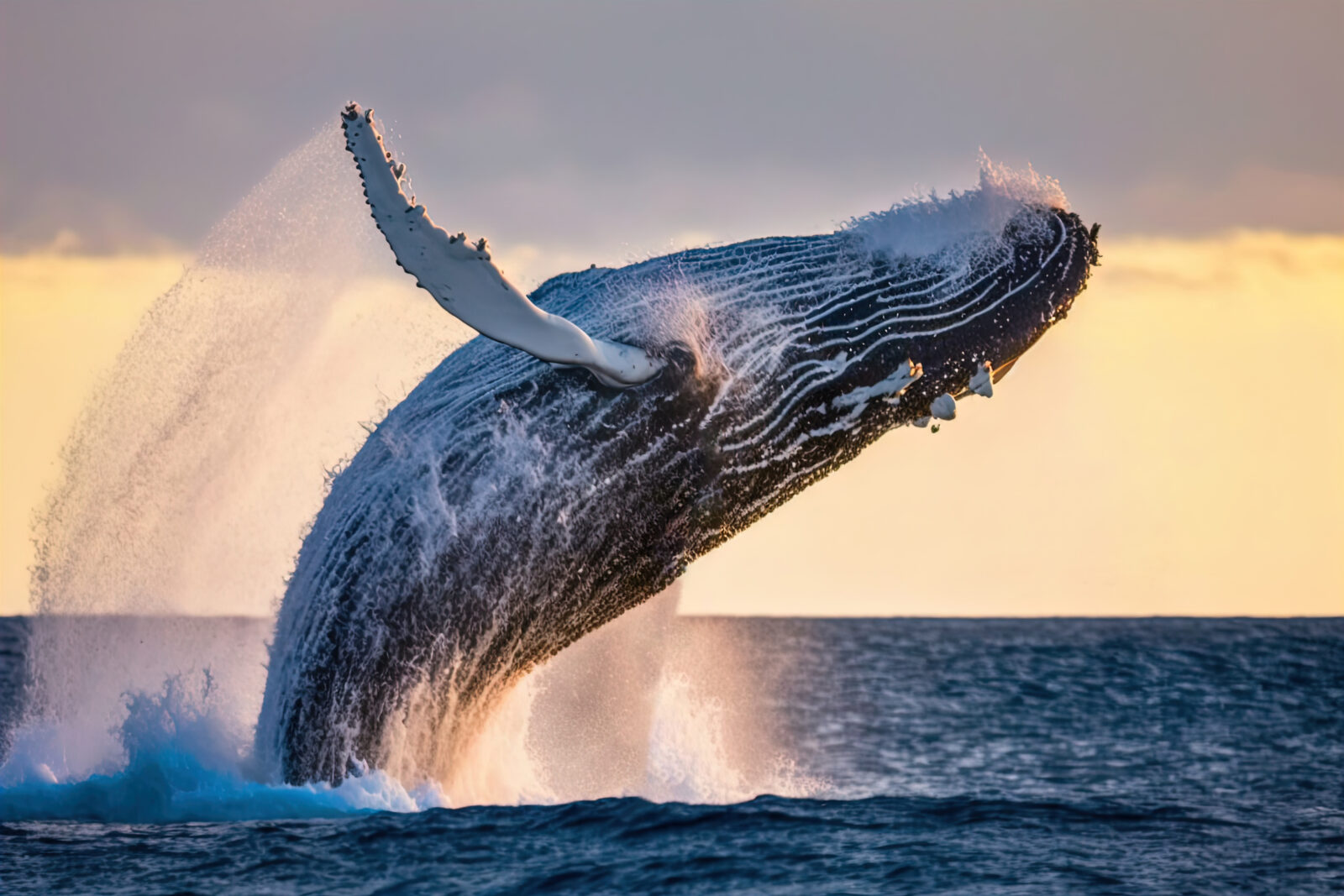


The Pentadactyl Whale Flipper: An Engineering Masterstroke

Is Adaptation Actually a Fight to Stay the Same?
Engineers Crash the Evolution Party, Rethink Biological Variation
On today’s ID the Future, physicist and engineer Brian Miller sits down with host Casey Luskin to survey exciting developments in intelligent design research that are driven by an engineering model for understanding and studying variations in species. ID researchers are pushing this work, but so too are systems biology researchers outside the intelligent design community. Tune in to hear Miller and Luskin discuss everything from fruit flies, finch beaks, and stickleback fish to mutational hotspots, phenotypic plasticity, and the gravity well model of biological adaptation.

Dustin Van Hofwegen on Engineering and Evolution in Lilliput
On today’s ID the Future we go behind the scenes at the recent Conference on Engineering in Living Systems, where host Jonathan Witt sat down with Dustin Van Hofwegen, a biology professor at Azusa Pacific University in California. The two discuss the private conference, which brought together biologists and engineers to study how engineering principles and a design perspective can and are being applied to biology — to plants and animals but also to Van Hofwegen’s area of focus, the Lilliputian realm of microbial biology. The two quickly move into a conversation about Van Hofwegen’s article in the Journal of Bacteriology, co-authored with Carolyn Hovde and Scott Minnich, based on research they did at the University of Idaho. As Van Hofwegen explains, the research focused on one of the most ballyhooed evolutionary changes to come out of Richard Lenski’s long-term evolution experiment at Michigan State University, a decades-long study of many thousands of generations of E. coli bacteria. Perhaps the biggest evolutionary development in the course of the experiment involved some bacteria beginning to feed in citric acid. Interesting, to be sure, but as Van Hofwegen explains, E. coli already has this capacity; it’s just a matter of switching it on. Van Hofwegen, Hovde, and Minnich demonstrated this through do-or-die experiments with E. coli, which led to the bacteria developing the capacity not in years or decades, as in the Lenski experiment, but in fourteen days, in as little as 100 generations. Van Hofwegen unpacks why this is an embarrassing result for Neo-Darwinism, then he and Witt discuss another study, this one focused on antibiotic resistance but with a similar result: the findings suggested that the antibiotic resistance observed came not by evolving anything new but by tweaking something already present — in this case, by actually breaking something.