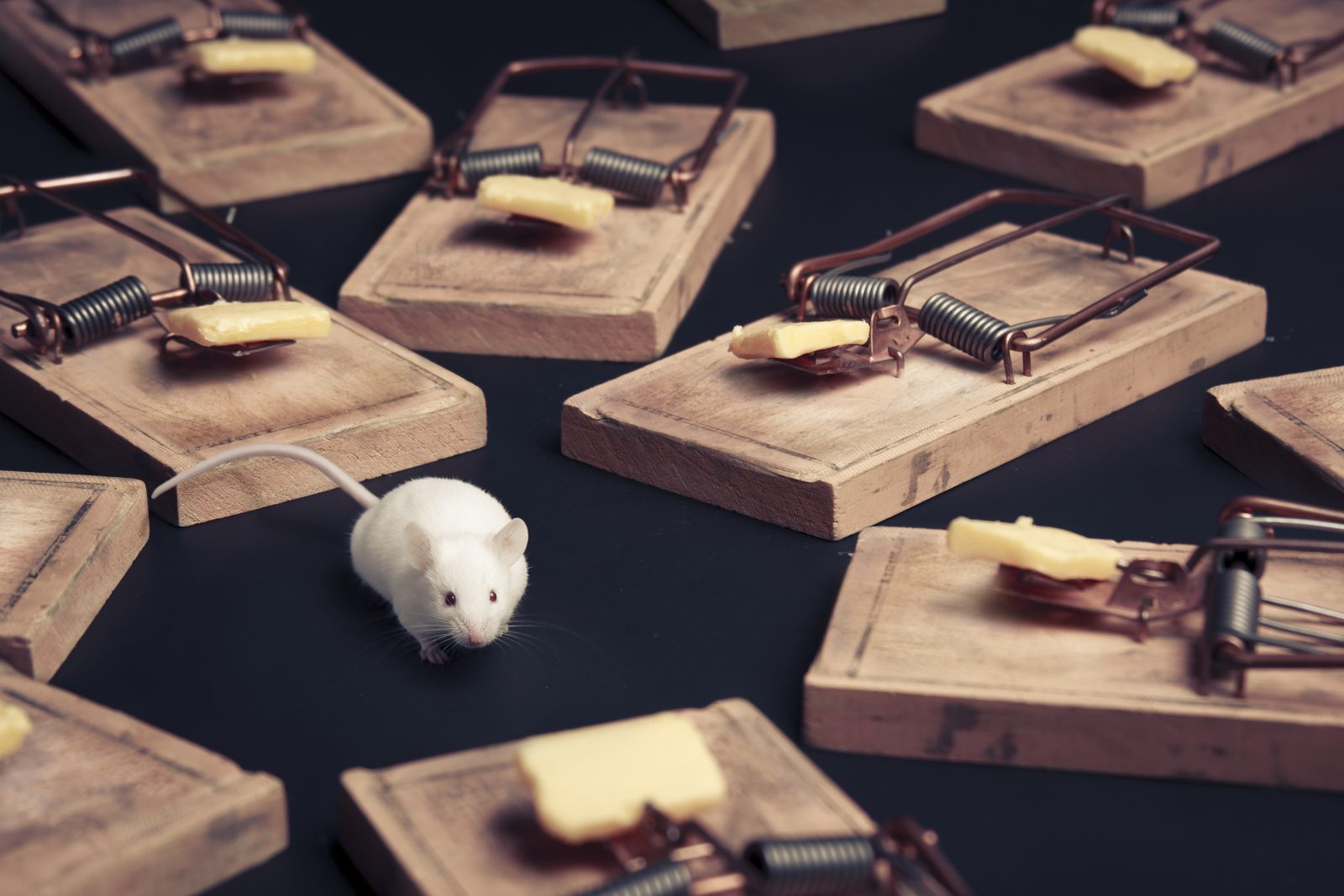
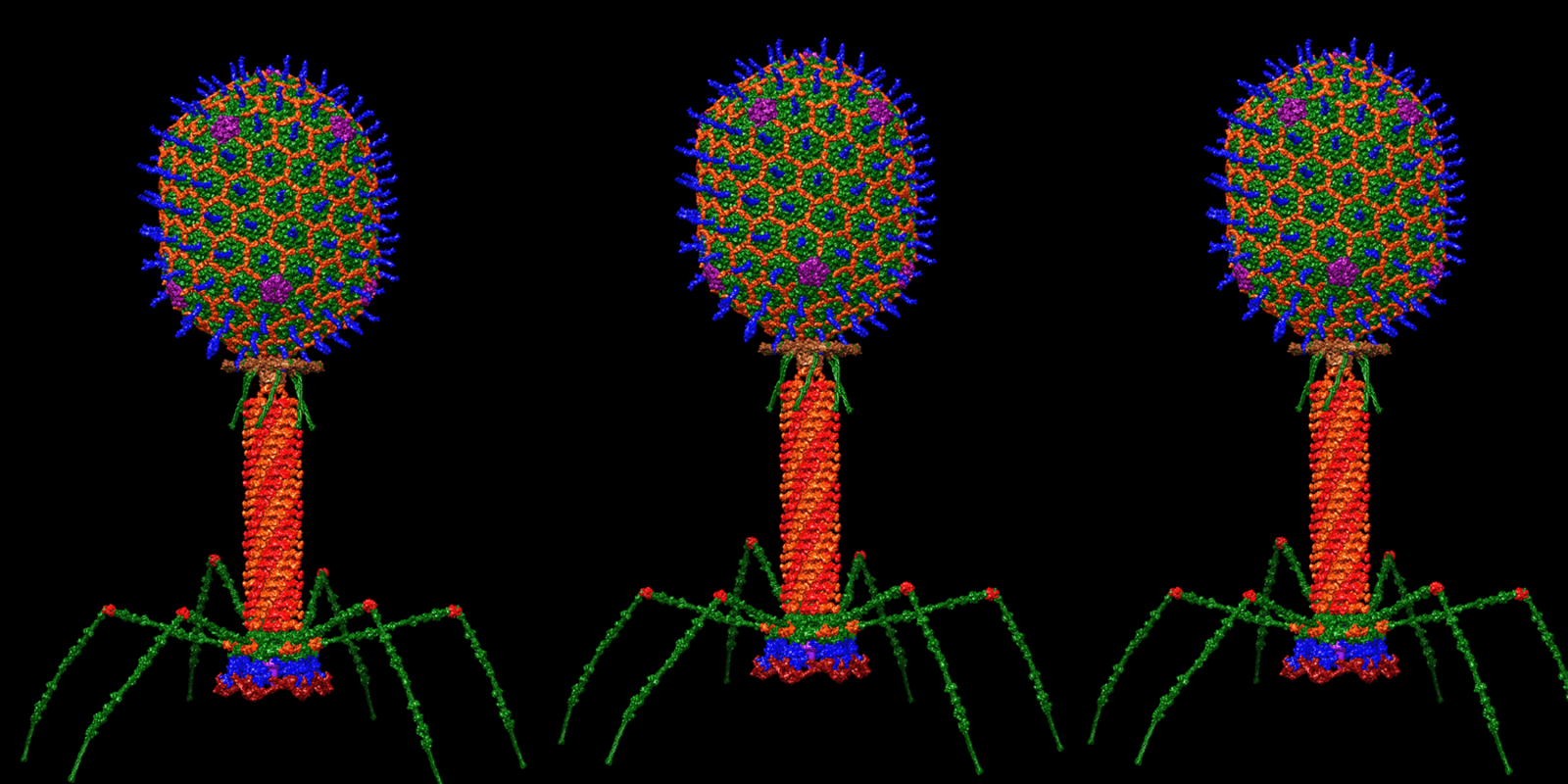
On today’s ID the Future, Lehigh University biologist Michael Behe argues that Darwinism was built on a foundation of ignorance. Through no fault of Darwin’s, neither he nor anyone else in his day had a clue about the nature of cellular life and biological information, says Behe. Even the biologists of the Neo-Darwinian synthesis in the first half of the twentieth century were fairly clueless about the foundation of life, Behe says. When researchers did finally begin to unravel the sophisticated foundations of life, earlier notions of how evolutionary processes might have invented the great diversity of life forms on earth were exposed as causally inadequate. Behe says that in fact all the attempts to rescue the idea of mindless macroevolution have been exposed as inadequate by our growing understanding of molecular biology, but evolutionary theory blithely sails along anyway, thanks to institutional inertia. A key defeater of the theory, Behe says, is captured by his concept of irreducible complexity. He explains the idea with a simple illustration, a mousetrap, and then applies it to a marvelous molecular machine that researchers have only recently come to appreciate, the Escherichia virus T4 bacteriophage. As he argues, this bacteriophage powerfully bespeaks the purposeful arrangement of parts, rather than mindless evolutionary processes. The occasion for his conversation with host Casey Luskin is his contribution to the recent Harvest House anthology, The Comprehensive Guide to Science and Faith. Image Credit: Dr. Victor Padilla-Sanchez: Atomic structural model of bacteriophage T4 in UCSF Chimera software using pdbs of the individual proteins.