Behe Counters the Best Objections to Irreducible Complexity and ID, Pt 3
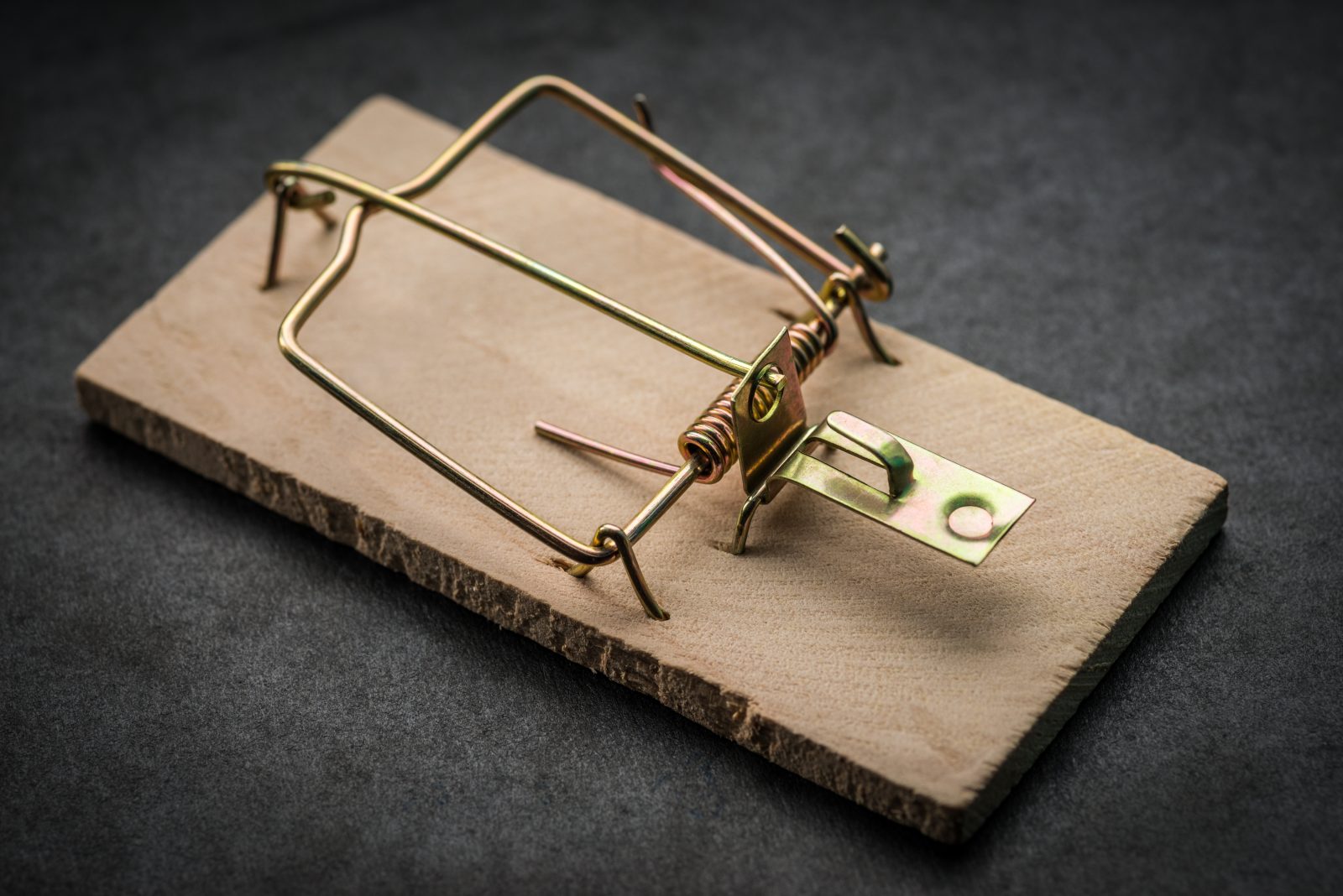
On today’s ID the Future biologist Michael Behe and Philosophy for the People host Pat Flynn conclude their conversation (posted by permission here) about some of the best objections to Behe’s central case for intelligent design. One objection Behe and Flynn tackle in this episode: the idea of evolution overcoming the irreducible-complexity hurdle through co-option. That is, maybe the precursors to what would become one of today’s molecular machines, such as the bacterial flagellum motor, co-opted simpler machines being used for other purposes, allowing evolution to build a bacterial flagellum motor one small step at a time over thousands or millions of generations, even though the completed bacterial flagellum ceases to function at all when just one of its many key parts is removed. Behe has illustrated the idea of irreducible complexity with a mechanical mousetrap. Take away just one of its several key parts and it ceases to function even a little bit as a mousetrap. Evolutionist Kenneth Miller counters by noting that parts of the mousetrap could have served other purposes, such as a paper weight or a tie clip. Listen in to hear Behe’s explanation as to why such imaginative reasoning is no help to the evolution of irreducibly complex biological wonders like the bacterial flagellum. At the end of the conversation, Flynn points listeners to a web page where he has gathered his several conversations with Behe over the years, including two that involved debates with pro-evolution guests. That page is here. Flynn also calls attention to Behe’s four books, including his latest one, where he answers many objections posed by his critics, with many of the critiques appearing in high-level science journals. The book is A Mousetrap for Darwin. You can get it here and here in hardcover, paperback, or Kindle/eBook.