

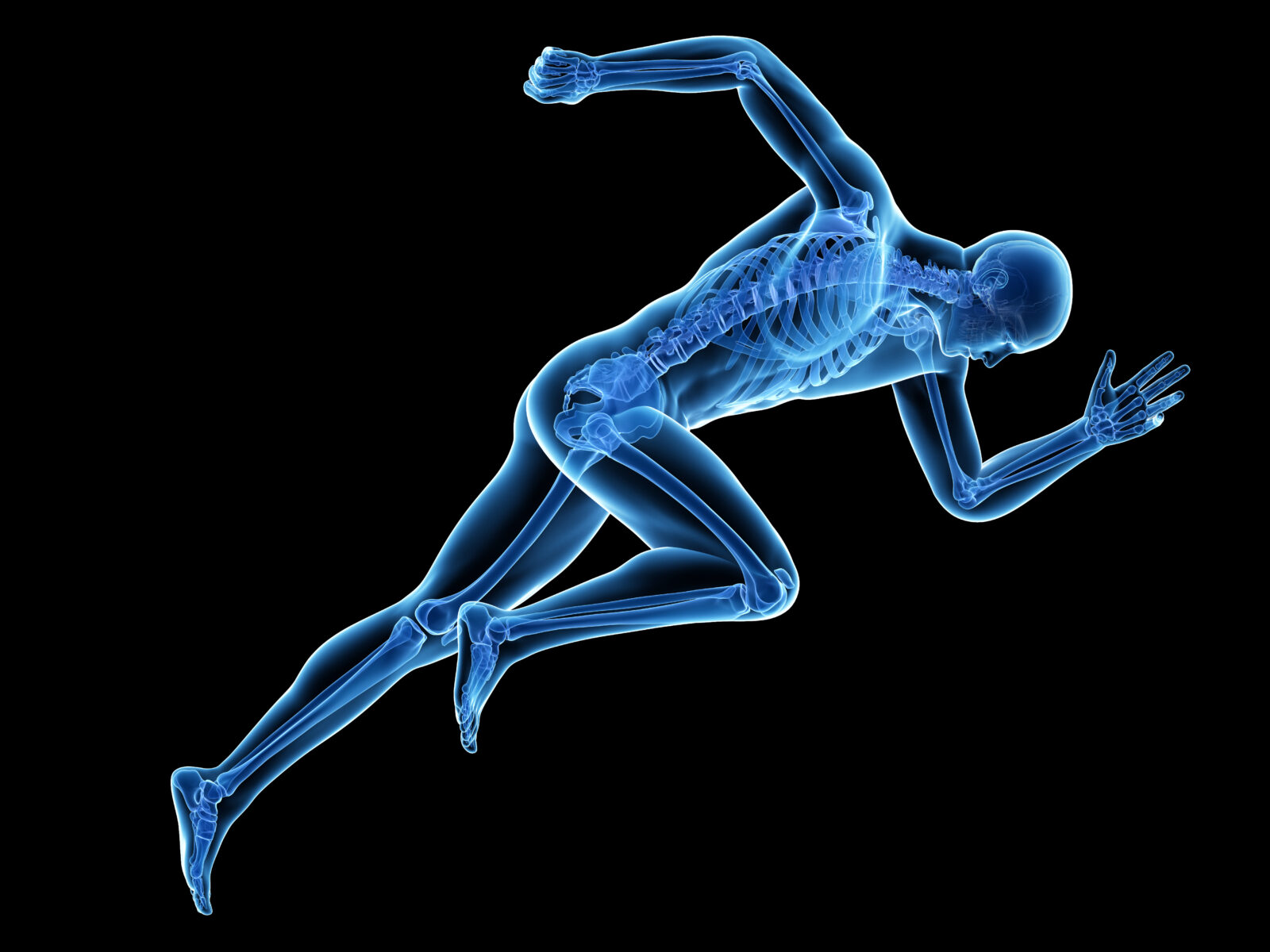
Engineering, not Evolution, Explains the Body

Human Skeletal Joints—Engineering Masterpieces, Pt. 2
Today’s ID the Future completes a talk by award-winning British engineer Stuart Burgess, who explains how the human ankle and wrist joints offer powerful evidence of engineering genius. Burgess is answering evolutionist Nathan Lents, who has argued that human joints are badly designed and, therefore, evidence against intelligent design and for Darwinian evolution’s blind trial-and-error process. According to Burgess, Lents ignores—and seems to be ignorant of—the many ingeniously engineered features of our joints, leading Lents to make easily refuted claims. For example, Lents says an ankle with fused bones would be a superior design to a healthy human ankle. Not if the person hopes to play squash or tackle any number of other activities that require the suppleness and responsiveness of the human ankle, Burgess notes. Burgess’s lecture was taped at the 2022 Westminster Conference on Science and Faith in the greater Philadelphia area. The conference was jointly sponsored by Westminster Theological Seminary and Discovery Institute’s Center for Science and Culture.

Darwin’s Rhetorical Foundation of Sand: Theological Utilitarianism
On this ID the Future, biophysicist Cornelius Hunter explores Charles Darwin’s theological arguments for his theory of evolution. By theological, Hunter doesn’t mean that Darwin was arguing for theistic evolution. He means that Darwin received what is known as theological utilitarianism from the intellectual culture of his youth, which had strong deistic tendencies and expected everything in creation to be perfectly adapted, and he made a case against it, presenting mindless evolution as a better explanation for his observations of the biological world than theological utilitarianism. But one problem with this approach, according to Hunter, is that it assumed that theological utilitarianism is THE alternative to blind evolution. In fact, there are other alternatives, including an orthodox Judeo-Christian understanding of God’s relationship to his creation. In Hunter’s conversation with host Casey Luskin, he unpacks the differences in this other understanding of God and shows how Darwin’s tunnel-vision fixation on theological utilitarianism led him into multiple problems. Hunter further shows that this basic theological mistake of Darwin’s also crops up in later defenders of Darwinism. Hunter and Luskin end the discussion by making what may strike some as a surprising claim: Evolutionary theory, argued in the way that Darwin and many of his followers argue the case, is fundamentally theology-based, whereas the theory of intelligent design, which points to a design of life and the cosmos, is strictly science-based. The occasion for the interview is Hunter’s chapter on this subject in the recent anthology co-edited by Luskin, The Comprehensive Guide to Science and Faith: Exploring the Ultimate Questions About Life and the Cosmos. Check it out.

Biologist Jonathan Wells Offers a Cure for Zombie Science
On this ID the Future, Zombie Science author and biologist Jonathan Wells and host Andrew McDiarmid explore the seductive but misleading appeal to consensus science. This is when someone makes a bandwagon appeal to support a scientific hypothesis rather than offering evidence and arguments—as in, “All serious scientists agree that X is the case.” Wells says history makes hash of the consensus-science appeal because the history of scientific progress is all about a consensus view being overthrown by a newer, more accurate view that for a time was a minority view. Wells also draws a distinction between evidence-based empirical science and ideologically driven science. The example he gives for the latter: scientific materialism. Instead of a search for truth about the natural world, science under scientific materialism becomes a search for the best materialistic explanation for this or that phenomenon. Mix scientific materialism and consensus science and you get what Wells has described as “Zombie Science.” Wells and McDiarmid also discuss the problem of science journalism hype. Most scientific discoveries are small, incremental findings of little interest to the general public. The solution for many science journalists: hype the small finding into something earth-shattering. As a remedy, Wells encourages a modest dose of skepticism anytime one is reading a science article in the popular press. What about the claims of Darwinists that the science “is settled,” that evolution “is a fact,” and that bad design in biology proves that hit-or-miss evolution is the maker of life’s diversity, not an intelligent designer? Here Wells encourages more than a modest dose of skepticism, and gives the example of the supposed “backward wiring of the vertebrate eye” as a case in point.

Darwin Devolves Author Michael Behe Tangles with Two Philosophers, Pt. 3
On this ID the Future, ID biologist Michael Behe continues fielding tough questions from philosophers Pat Flynn and Jim Madden. Here in Part 3 of 3, Behe responds to the claim that some designs in biology are bad designs and to criticisms leveled at ID from some Thomists. Also in the mix, the issue of academic pressure to distance oneself from ID, even before those involved understand what the theory of intelligent design actually is. Madden also asks Behe what reforms he’d pursue if he suddenly found himself in charge of the National Academy of Sciences. Tune in to hear Behe’s response, and much more. This three-part series is borrowed, with permission, from Flynn’s podcast, which can be found on his YouTube channel.